Universal Design and Accessibility
Table Of Content
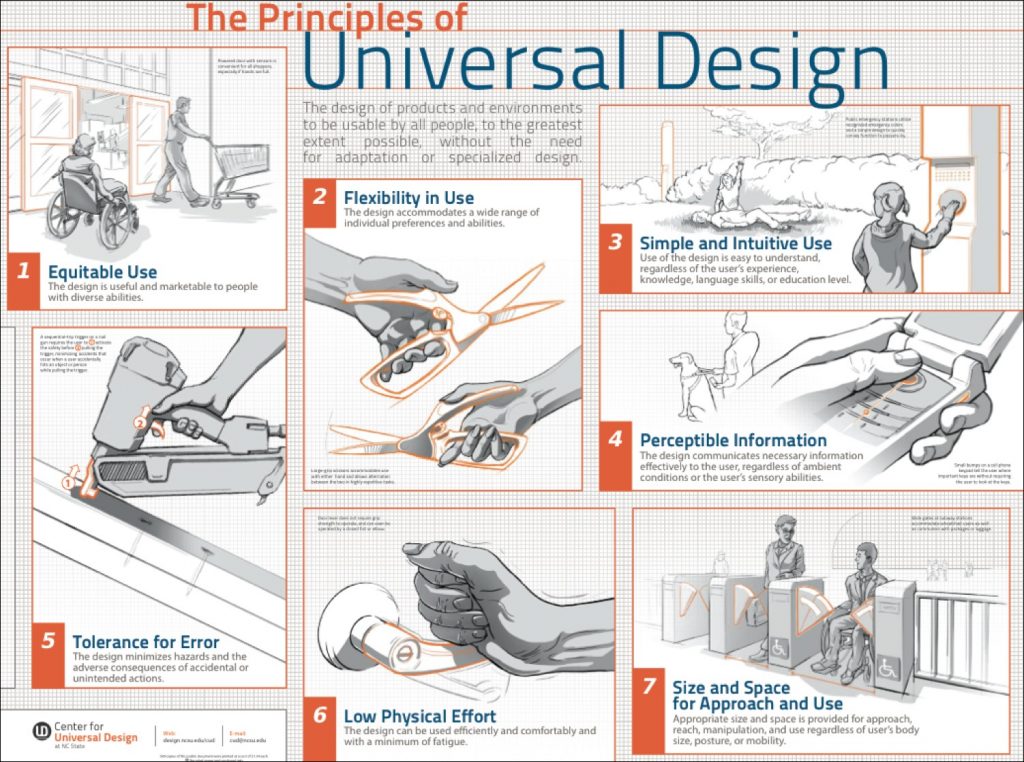
Examples of more narrowly defined scopes are applications of UD to online learning, informal science learning, student services, IT, or physical spaces. The goal of Universal Design is to maximize usability by individuals with a wide variety of characteristics. Whether we are talking about learning strategies or physical space, Universal Design operates by a set of principles designed to maximize access by everyone. This four-part video series provides an introduction to Universal Design for content creators, developers, managers and procurement professionals. It includes resources, tips, and tricks for designing products and environments to be usable by all people, to the greatest extent possible, without the need for adaptation or specialized design.
Simple and Intuitive Use Guidelines
Collects anonymous data on how you navigate and interact, helping us make informed improvements. You’ll enjoy a smoother, more personalized journey without compromising your privacy. We share user ID with Bugsnag and NewRelic to help us track errors and fix issues. Chukwuebuka is an architecture student and an amateur writer using his skills to express his ideas to the world.
Full Article - Society of Behavioral Medicine
Full Article.
Posted: Fri, 20 Dec 2019 09:49:16 GMT [source]
Equitable Use Guidelines
Of the proactive design approaches, there is no approach that addresses greater user diversity than universal design (UD). A great example of how these three sets of principles can be integrated together is when designing a class. Universal design principles can apply to lectures, classroom discussions, group work, handouts, web-based instruction, fieldwork, and other academic activities. The 7 Principles of Universal Design were developed in 1997 by a working group of architects, product designers, engineers and environmental design researchers, led by the late Ronald Mace in the North Carolina State University (NCSU). The purpose of the Principles is to guide the design of environments, products and communications.
Understand the Social Needs for Accessibility in UX Design
We appreciate your interest in Universal Design, a global movement of inclusive design practice initiated at NC State University College of Design. The Center for Universal Design is currently not active due to funding challenges. This update will focus specifically on addressing systemic barriers that result in inequitable learning opportunities and outcomes. CAST aims to develop a transparent, inclusive, and community-driven process. If you are interested in collaborating and staying updated on our progress, we invite you to complete a brief survey.
Twitter is an online social networking service, which allows users to send and read messages of 280 characters or less. Here is Twitter’s sign-up form with error messages for input format validation errors. It checks for correct email and password format.© Twitter, LLC., Fair Use. Explore more of the Universal Design vs. Inclusive Design aspect in this insightful article by Genís Frigola Universal design, inclusive design, and equity-focused design.

What’s more, you’ll also come away with the knowledge to conduct effective accessibility testing through working with users with disabilities. Although applying universal design of instruction (UDI) does not eliminate the need for special accommodations—e.g., a sign language interpreter for a deaf student—it does ensure full access to the content for most students. By applying UDI in courses as they are created, educators minimize the need to make accommodations later. For example, letting all students have access to your class notes and assignments on an accessible website can eliminate the need for providing materials in alternate formats. For more information on accommodations and examples of what to plan for, visit our Accommodations pages.
Tips on How To Make a Website Digitally Accessible
For example, a captioned video will allow people to choose to listen or to read in order to understand content. This not only provides access to individuals with hearing impairments but also accommodates those who would rather not use sound or who comprehend better through reading. Universal design is often mentioned (or confused) with related concepts like accessibility and inclusive design. While accessibility refers to designs that specifically accommodate those with physical and cognitive disabilities, universal and inclusive design go beyond that.
Popular Mistakes in Universal Web Design — SitePoint - SitePoint
Popular Mistakes in Universal Web Design — SitePoint.
Posted: Wed, 20 Jul 2011 07:00:00 GMT [source]
WordPress’s homepage offers users generous amounts of space to access desired dropdowns (at the top of the webpage). Evernote’s homepage offers flexibility in use via options to select. Users can approach Evernote in different contexts, for personal projects or for professional, team-based ones. Bluetooth’s homepage has an option to select the language (world icon, top right).
Universal design vs. inclusive design
So… what is a proven and pain-free way to well-executed accessibility? If you’ve ever tried to optimize your site or app for accessibility, you’ll know it can be a complex and intimidating task… and it can therefore be very tempting to leave it until last or, worse still, avoid it altogether. By understanding that accessibility is about more than just optimizing your code, you’ll find you can build it into your design process. This will ensure you are taking a disability advocacy approach, and keeping the focus on your users throughout the development process. One of the challenges in the current state of applications of UD, UDL, UD of IT, is the three different communities engaged in most efforts in each category rarely talk to one another. The scope of applications of UD in Higher Education (UDHE) includes all products and environments that directly or indirectly support teaching and learning in higher education.
A small target area can be a problem on mobile devices because it is more difficult to select with precision. According to an MIT Touch Lab study in 2003, the average size of a human adult index finger is 1.6 to 2 cm. Converting that, we have approximately 60–76 pixels on a digital screen.
Thus, you should incorporate them into any project you do from the very beginning. For product designers, their focus is on form factors such as the size of and space involved with the product. As digital designers, our focus is less on form factors but more on what is on the screen. This is a shortsighted mindset because it is important to think outside of the screen and consider our users’ environment as well, especially as users view websites not only on desktops but also—increasingly—on mobile devices as well.
Uber’s ultra-easy Ride section offers users the quick convenience of pickup location and destination. Software includes on-screen control buttons that are large enough for students with limited fine motor skills to select. Governs the storage of data necessary for maintaining website security, user authentication, and fraud prevention mechanisms.
Comments
Post a Comment